Magnetic Drive Pump Sliding Bearing Failure Issue
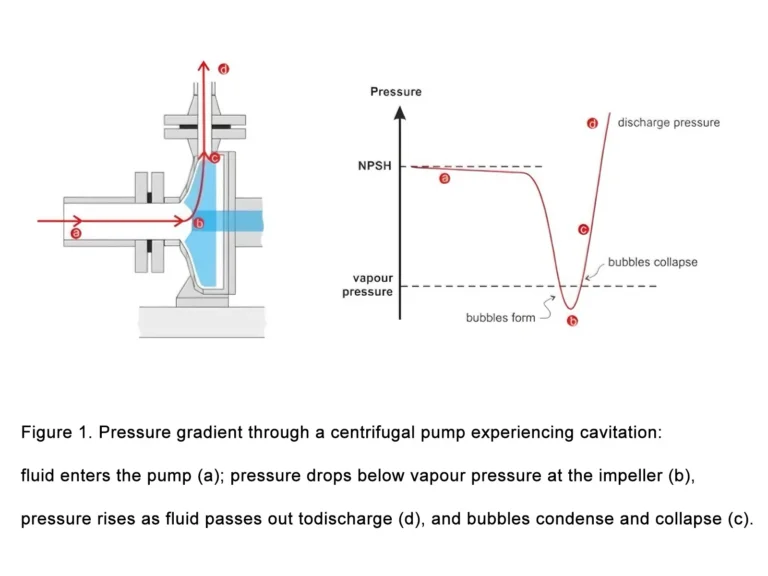
According to the working principle and structural characteristics of magnetic drive pumps, frequent sliding bearing damage is usually related to the following magnetic drive pump failure causes: impurities entering the bearing clearance, insufficient lubrication caused by fluid interruption, and cavitation caused by medium vaporization.
Therefore, it is necessary to systematically analyze the causes of sliding bearing damage from the aspects of process conditions, pump installation methods, and operation practices.
Below, We take crystallization faults and magnetically driven pumps for transporting isopentane as examples to analyze magnetic drive pump failure causes and solutions.

Analysis of Sliding Bearing Failure Causes
Analysis of Sliding Bearing Failure Causes of Magnetic Drive Pumps Conveying Acid and Alkali Media
Elimination of Conventional Operation and Installation Factors
After inspection, the following conditions were confirmed:
- The liquid levels of the acid and alkali storage tanks were all within the upper limits of process requirements, and no dry-running condition occurred.
- No debris or blockage was found in the pump inlet filter, eliminating the possibility of impurities as one of the magnetic drive pump failure causes.
- Pump alignment met technical requirements, and no bearing damage caused by excessive vibration was found.
Direct Cause Analysis of Bearing Failure
After disassembling and inspecting the magnetic drive pump, obvious crystalline substances were found inside the pump chamber. It was determined that crystallization was the main magnetic drive pump failure cause leading to sliding bearing damage.
Analysis of Crystallization Causes
Cause 1: Pump Operating Temperature Close to the Medium Crystallization Point
- Crystallization point of 32% caustic soda: 5.4°C.
- Crystallization point of 98% concentrated sulfuric acid: 0.1°C.

The original design only installed heating systems inside the acid and alkali pump room. Due to the need for nitrogen purging of acid and alkali pipelines and safety requirements for good ventilation, the windows of the pump room could not be fully closed. As a result, the pump operating temperature was close to the crystallization point of the medium for long periods, leading to crystallization, which became one of the common magnetic drive pump failure causes.
Cause 2: Long-Term Low-Temperature Nitrogen Purging
In the process design, acid and alkali pipelines are purged with nitrogen for a long time. The low-temperature nitrogen further reduces the medium temperature and intensifies crystallization. The crystallized solids jam the sliding bearings, eventually causing bearing damage.
Analysis of Sliding Bearing Failure Causes of Magnetic Drive Pumps Conveying Isopentane

- Elimination of Impurities and Installation Issues.
- Inspection of the pump inlet filter showed no debris or blockage.
- Inspection of pump alignment showed all indicators were normal.
- These inspections ruled out impurities and vibration-related magnetic drive pump failure causes.
Main Cause Analysis of Bearing Failure
During inspection of the unloading operation, the following conditions were found:
- Low liquid level in the tank truck.
- Severe fluctuations of the pump outlet pressure gauge in the later stage of unloading.
- Obvious liquid flow interruption.
The sliding bearings of magnetic drive pumps rely on the conveyed medium for lubrication. Since isopentane unloading adopts a self-pressure unloading method, the medium becomes insufficient in the later unloading stage, causing flow interruption and poor lubrication of the sliding bearings. This is a typical magnetic drive pump failure cause when conveying isopentane, ultimately leading to bearing damage.
Solutions for Sliding Bearing Failure
Process and Equipment Improvement Measures
- Independently install heat tracing hoses for acid and alkali magnetic drive pumps to increase the internal medium temperature and prevent crystallization-related magnetic drive pump failure causes.
- Regularly clean the pump inlet filter to prevent crystallized substances or impurities from entering the pump chamber.
Process Operation Optimization Measures
- From a production operation perspective, shorten the duration of low-temperature nitrogen purging to reduce crystallization of acid and alkali media.
- During isopentane unloading, avoid completely emptying the tank and maintain a certain liquid level to ensure proper lubrication of the sliding bearings and reduce magnetic drive pump failure causes.
Magnetic Drive Pump Operation and Startup Requirements
Pre-Startup Inspection Requirements
- Before startup, the pump shaft must rotate smoothly by hand. If any resistance is found, the cause must be identified and eliminated immediately. Forced startup is strictly prohibited.
- When the pump installation position is below the liquid level, the suction valve must be opened before startup to fully fill the pump chamber with liquid.
- When the pump installation position is above the liquid level, the pump must be primed or vacuum exhaust must be applied before startup. Dry running is strictly prohibited.
Startup and Operation Requirements
- Close the outlet valve during startup and jog the motor to confirm that the rotation direction matches the arrow on the pump body. Reverse rotation is strictly prohibited.
- After startup, slowly open the outlet valve to allow the pump to gradually enter normal operating conditions.
- When the outlet valve is closed, continuous pump operation must not exceed 1 minute.
Abnormal Operating Condition Handling Requirements
- If pump flow rate and head do not reach rated values as motor speed increases, the pump must be stopped immediately.
- Re-prime and exhaust the pump to ensure the pump body and suction pipeline are completely filled with liquid before restarting.
- Only when the motor reaches rated speed and the pump flow rate and head enter the designed operating range can the pump be considered to be operating normally.
الخاتمة
The above analysis uses an isopentane conveying case to systematically explain magnetic drive pump failure causes and solutions.
If you have technical questions or new pump procurement plans, you are welcome to contact us. Our professional team can help you solve any pumping-related problems.
البريد الإلكتروني: jade@changyupump.com
الهاتف +86-13651913727