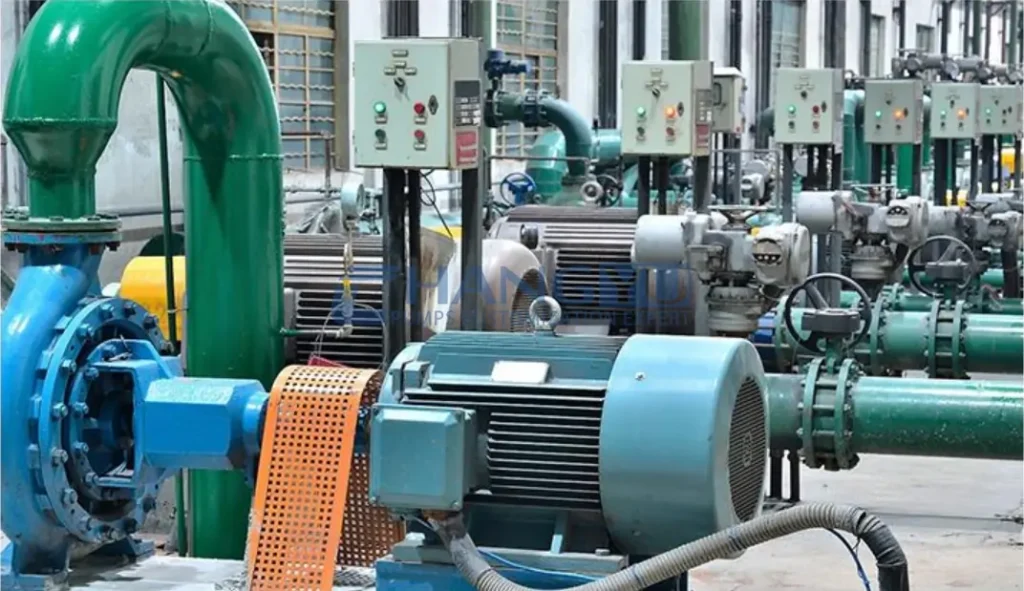
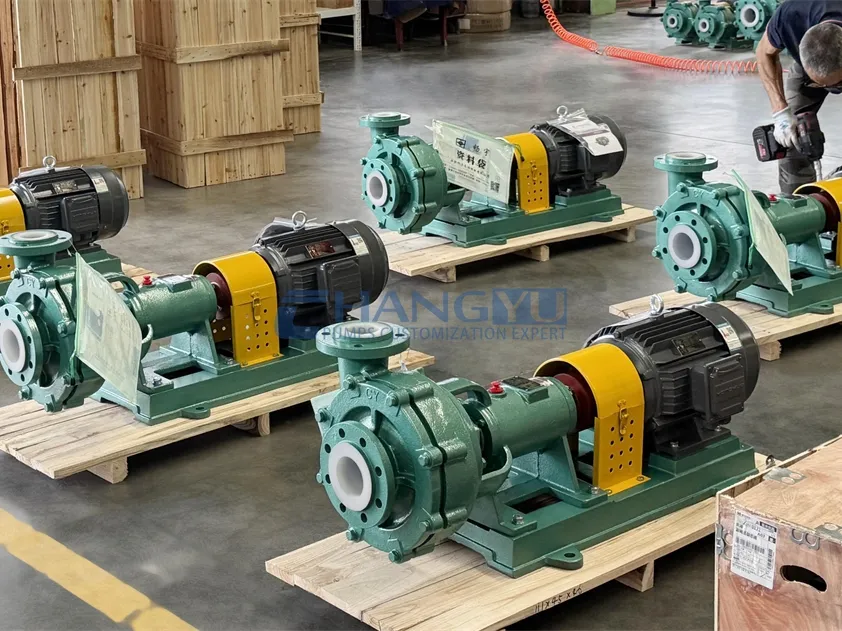
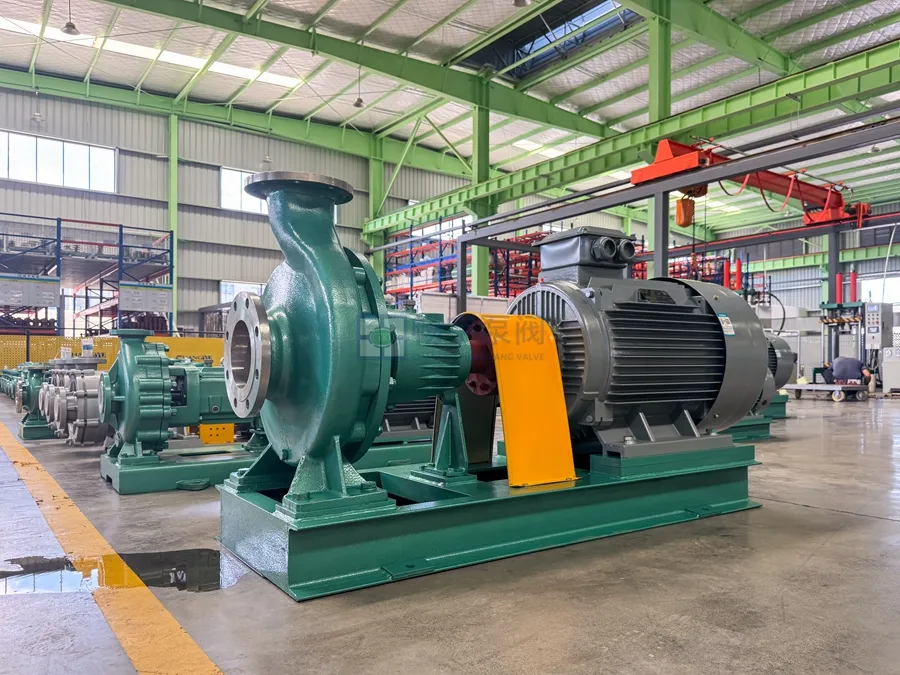
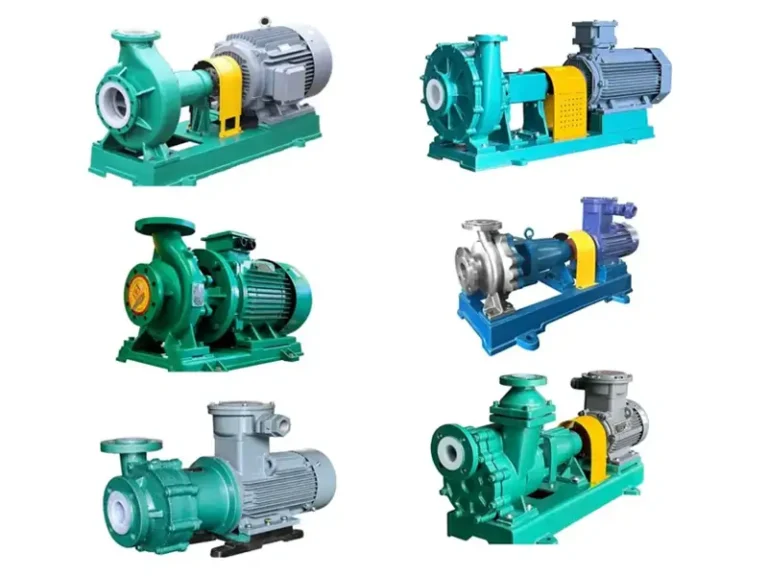
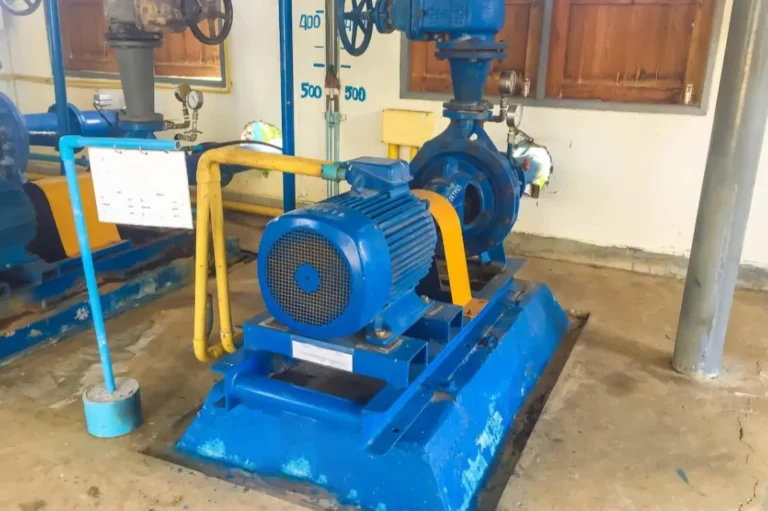
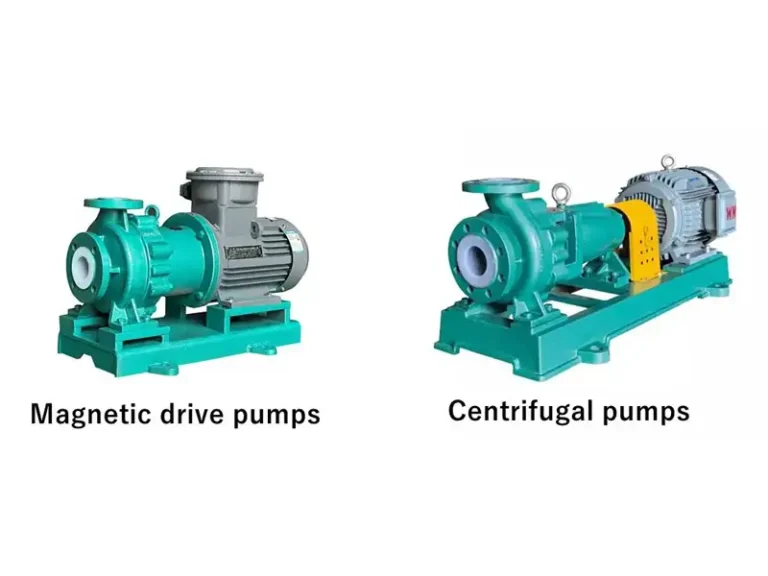
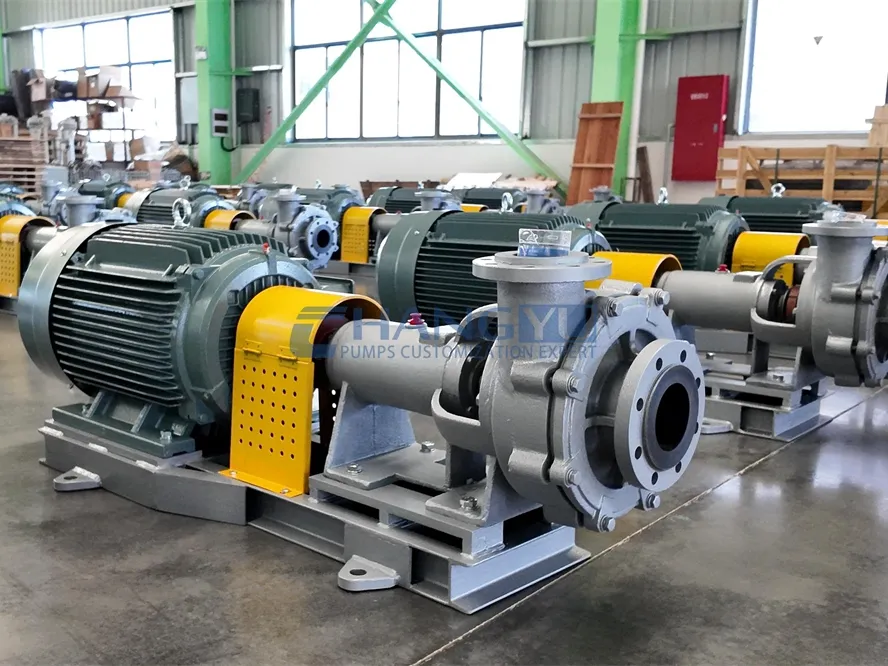
Industrial centrifugal pumps play a vital role in chemical processing, mining, environmental protection, new energy, and other harsh-duty industries. Especially for applications involving corrosive liquids and fluids containing up to 40% fine solids, selecting the right pump based on key performance parameters is critical for stable and efficient operation.
This article explains the core concepts of flow rate, head, rated power, shaft power, suction head, and discharge head, and shows how they relate to corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant industrial centrifugal pumps.
 Industrial Slurry Pumps
Industrial Slurry Pumps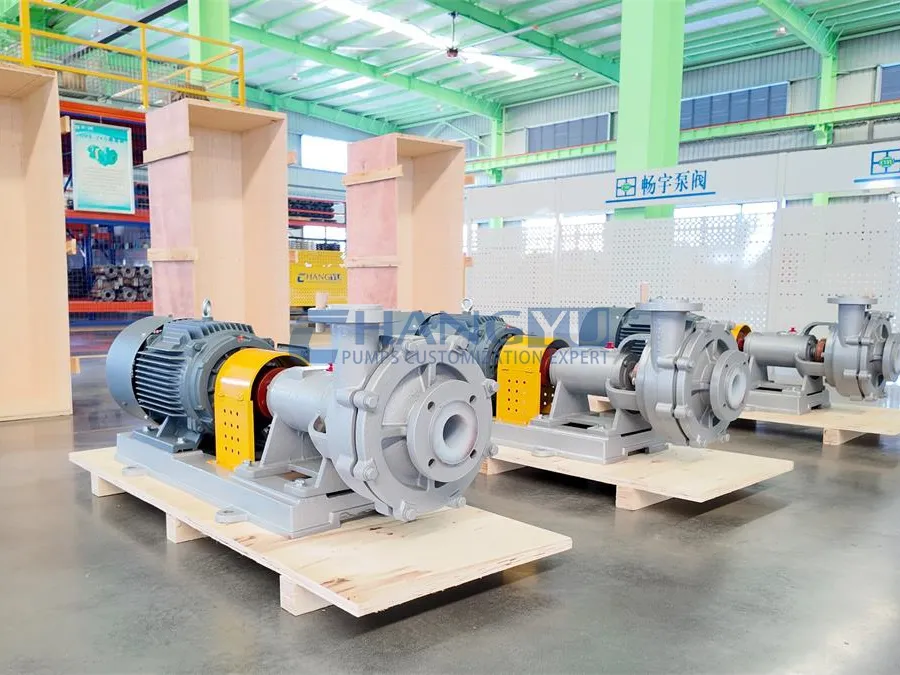 Desulfurization Circulation Slurry Pumps
Desulfurization Circulation Slurry Pumps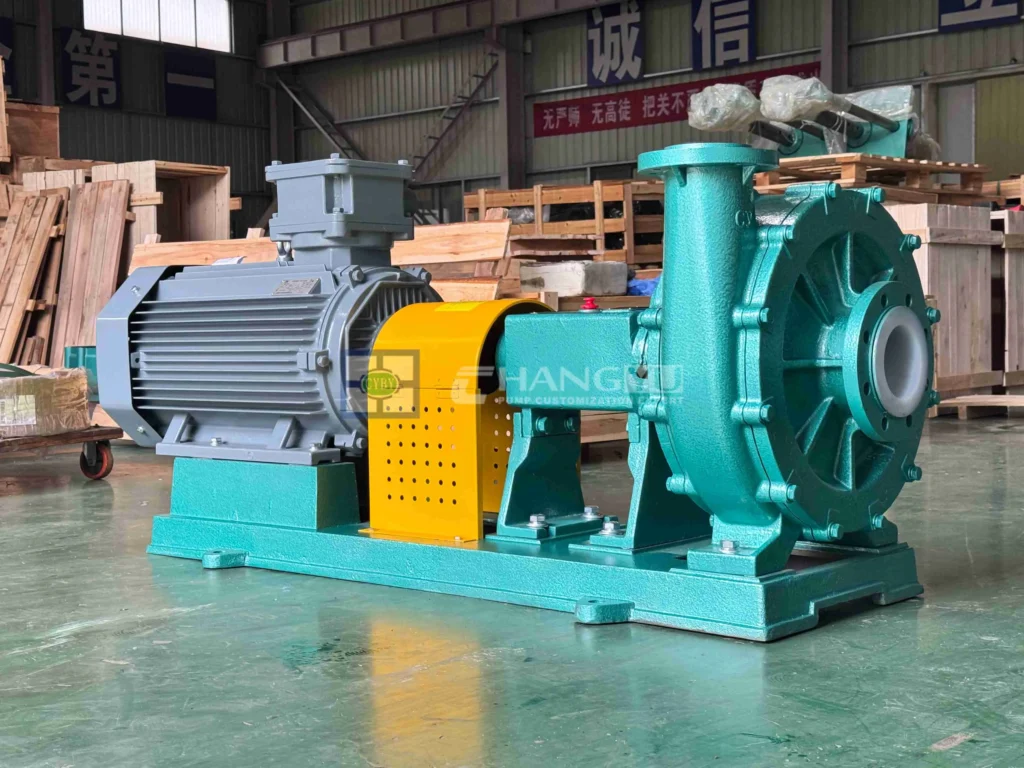 Chemical Transfer Pump
Chemical Transfer Pump
What Is an Industrial Centrifugal Pump?
A water pump or industrial centrifugal pump is a mechanical device that transfers liquid or increases its pressure by converting mechanical energy from a motor into kinetic and pressure energy through a rotating impeller.
Our industrial centrifugal pumps are specially designed with:
- Flow-through components are typically manufactured using steel-lined ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE).
- All pump casing components are optimized for handling highly corrosive fluids.
- Equipped with Changyu’s independently developed new double-ended mechanical seal, it ensures stable, leak-free operation when conveying corrosive fluids.
- Capable of handling fluids containing ≤40% fine solid particles.
Key performance parameters include:
Flow rate (Q), Head (H), Power (P), and Efficiency (η).
Flow Rate (Q): How Much Liquid the Pump Delivers
Flow rate refers to the volume of liquid delivered by the pump per unit time.
Common units: m³/h, m³/s, L/s, t/h.
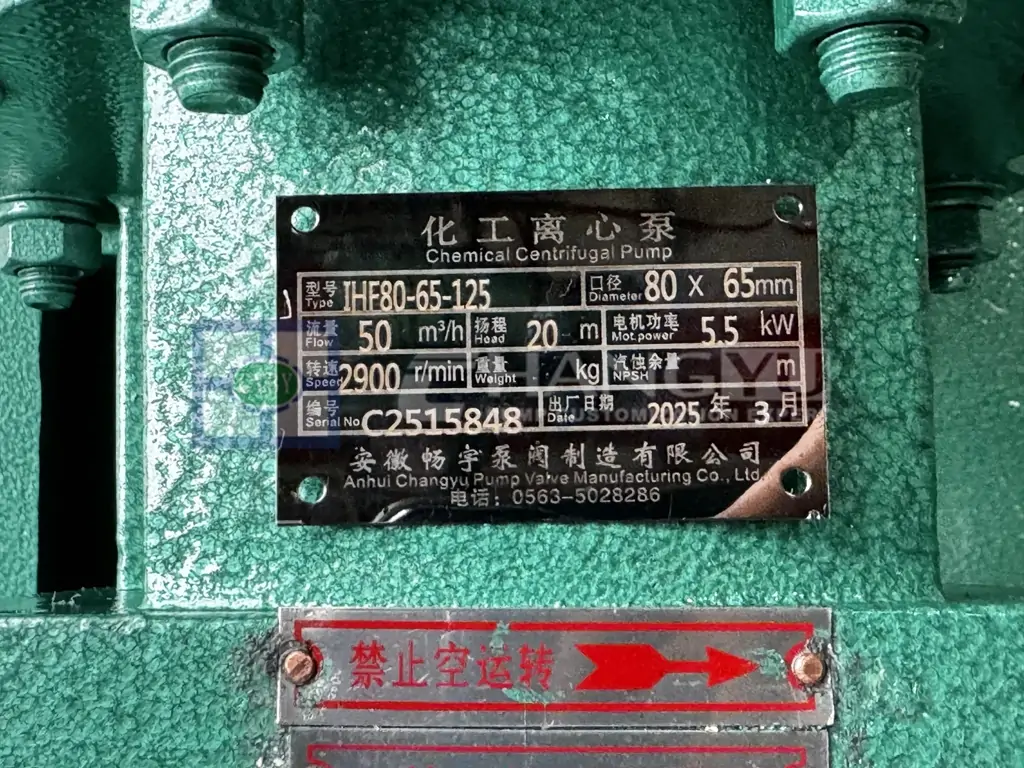
- The flow marked on the pump nameplate is the rated flow.
- Pumps achieve their highest efficiency near this point.
For slurry and corrosive media, maintaining stable flow ensures:
- Less wear on the impeller and casing
- Reduced risk of clogging
- Longer service life
Our wear-resistant centrifugal pumps are optimized to maintain stable flow even when handling solid-laden fluids.
Head (H): How High or How Far the Pump Can Deliver
Pump head is the energy added to the liquid by the pump, usually expressed as the vertical height the liquid can be lifted (m).
For centrifugal pumps:
- Suction head:
The vertical distance from the liquid source surface to the pump impeller centerline. - Discharge head:
The vertical distance from the pump impeller centerline to the discharge liquid surface.
Total head = Suction head + Discharge head
The head shown on the nameplate is the rated head, corresponding to the rated flow.
In corrosive and slurry applications:
- An adequate head ensures reliable transport through long pipelines.
- Our pumps feature an optimized and upgraded pump body along with high-quality impellers that are corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and capable of withstanding high temperatures. They maintain heads even when pumping corrosive fluids containing particles.
Rated Power: Motor Power Required for Safe Operation
Rated power usually refers to the motor power selected to drive the pump safely under rated conditions.
It must be:
- Higher than the pump’s shaft power
- Able to cover possible fluctuations in flow, head, and fluid density
For corrosive and high-solid fluids:
- Fluid density and viscosity may be higher than clean water.
- We select motors with proper margins to ensure continuous, overload-free operation.
Shaft Power (P): Actual Power Consumed by the Pump
Shaft power is the mechanical power transmitted from the motor to the pump shaft.
Not all shaft power becomes useful output — part is lost due to:
- Hydraulic losses
- Mechanical friction
- Leakage
Shaft power is a key reference for:
- Motor selection
- Energy consumption estimation
In slurry and corrosive pumps, shaft power is often higher than water pumps due to increased resistance and wear.
Our industrial centrifugal pumps use optimized hydraulic design and high-strength bearings to reduce power loss while handling abrasive media.
Pump Efficiency (η): How Effectively Power Is Used
Pump efficiency is defined as:
Efficiency = Useful hydraulic power / Shaft power
It reflects how well the pump converts input energy into liquid energy.
Efficiency consists of:
- Hydraulic efficiency (ηh) – losses in flow passages
- Volumetric efficiency (ηv) – leakage losses
- Mechanical efficiency (ηm) – bearing, seal, and disc friction losses
Overall efficiency:
η = ηh × ηv × ηm
Advantages of our corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant pumps:
- The lining process utilizes imported materials, which are sintered at high temperatures to form an integrated structure, minimizing hydraulic losses to the greatest extent possible.
- Reliable mechanical seals, auxiliary impeller seals, and dynamic seals reduce leakage.
- Heavy-duty bearings minimize mechanical wear.
This ensures stable efficiency even in harsh slurry service.
 Magnetic Centrifugal Pump
Magnetic Centrifugal Pump Stainless Steel Centrifugal Pump
Stainless Steel Centrifugal Pump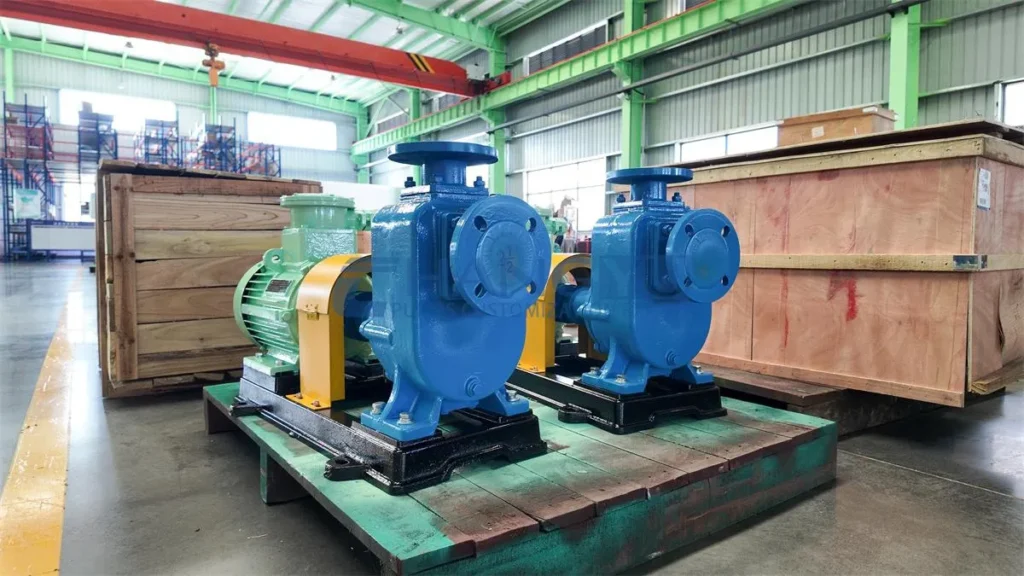 Self-priming Pump
Self-priming Pump
Why These Parameters Matter for Corrosion-Resistant Slurry Pumps
When selecting an industrial centrifugal pump for corrosive or abrasive fluids, these parameters directly determine:
- Whether the pump can meet process requirements
- Whether it can run efficiently long term
- Whether wear and corrosion will be controlled
- Whether operating costs stay low
For fluids containing up to 40% fine solid particles, it is especially important to match:
- Flow rate to prevent settling
- Head to overcome pipeline resistance
- Shaft power to handle a higher load
- Materials to resist corrosion and abrasion
Our pumps are engineered to meet these challenges in industries such as:
- Chemical processing
- Mining and metallurgy
- Environmental protection & wastewater
- New energy materials (lithium, battery slurry, etc.)
Conclusion
Understanding rated power, shaft power, suction head, discharge head, flow rate, and efficiency is essential for choosing the right industrial centrifugal pump.
For demanding applications involving corrosive liquids and solid-laden slurries, selecting a pump with proven corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and stable hydraulic performance ensures long service life and reliable operation.
If you are handling fluids with fine particles up to 40% and require a durable industrial centrifugal pump solution, our pumps are designed to deliver safe, efficient, and long-term performance.
If you have any questions regarding product selection or technical specifications, feel free to contact us now. Our professional technical team is ready to assist you.
Email: jade@changyupump.com
Phone: +86-13651913727