Is a Centrifugal Pump a Positive Displacement Pump? The answer is NO. They are two different types of pumps. Below, let’s understand their main differences and application scenarios. Changyu Pump helps you distinguish what is a Centrifugal Pump and what is a Positive Displacement Pump.
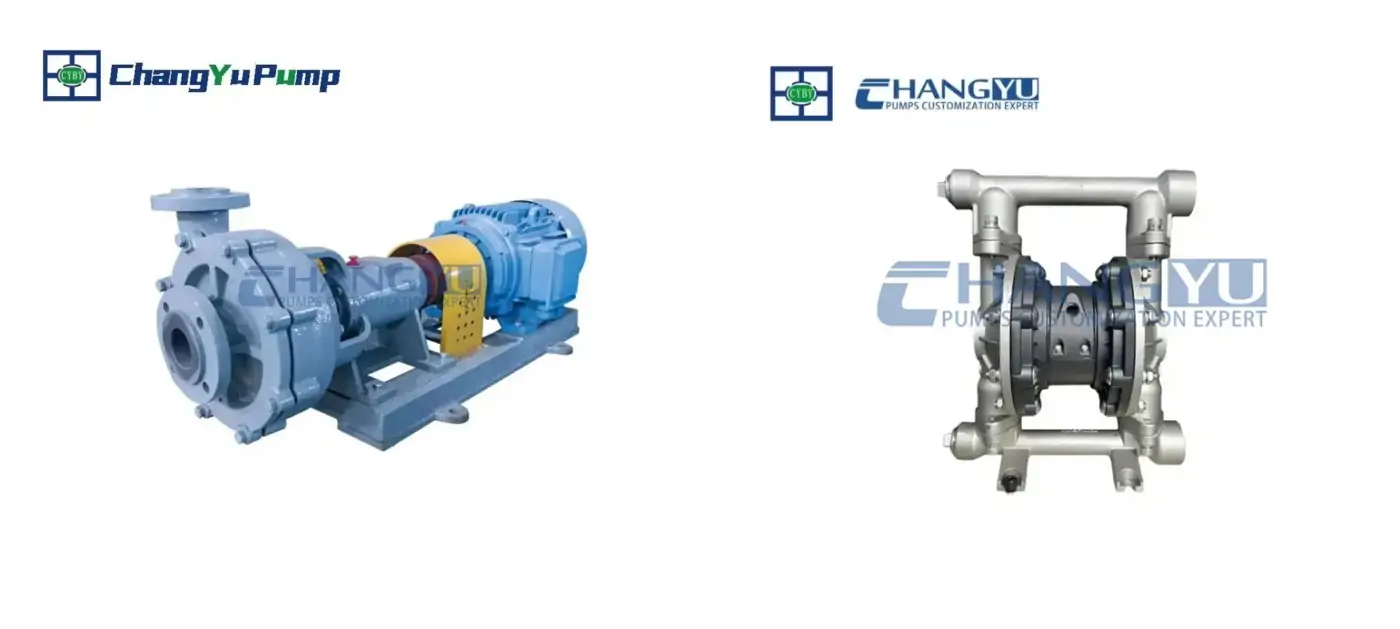

What is a Centrifugal Pump?
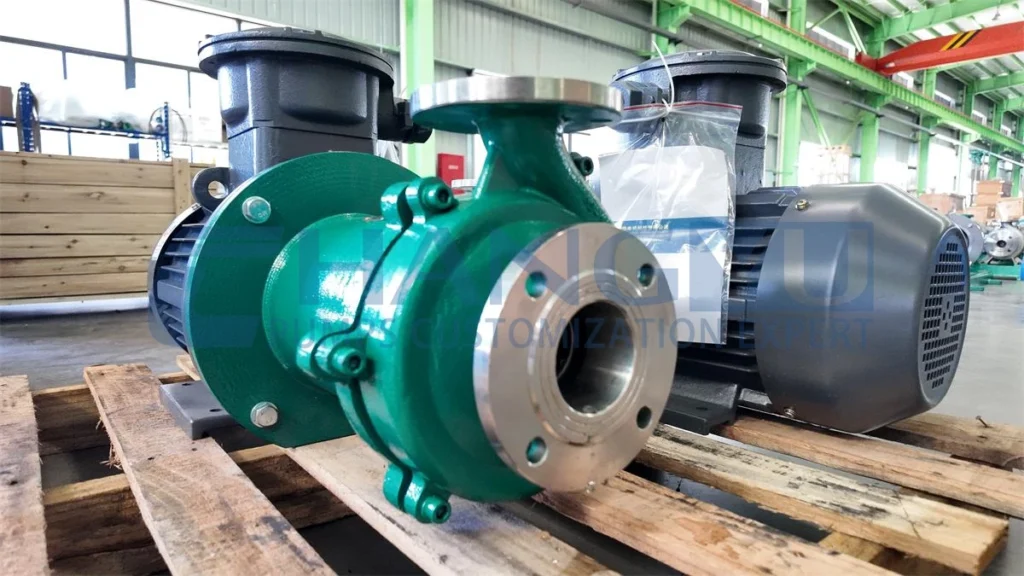
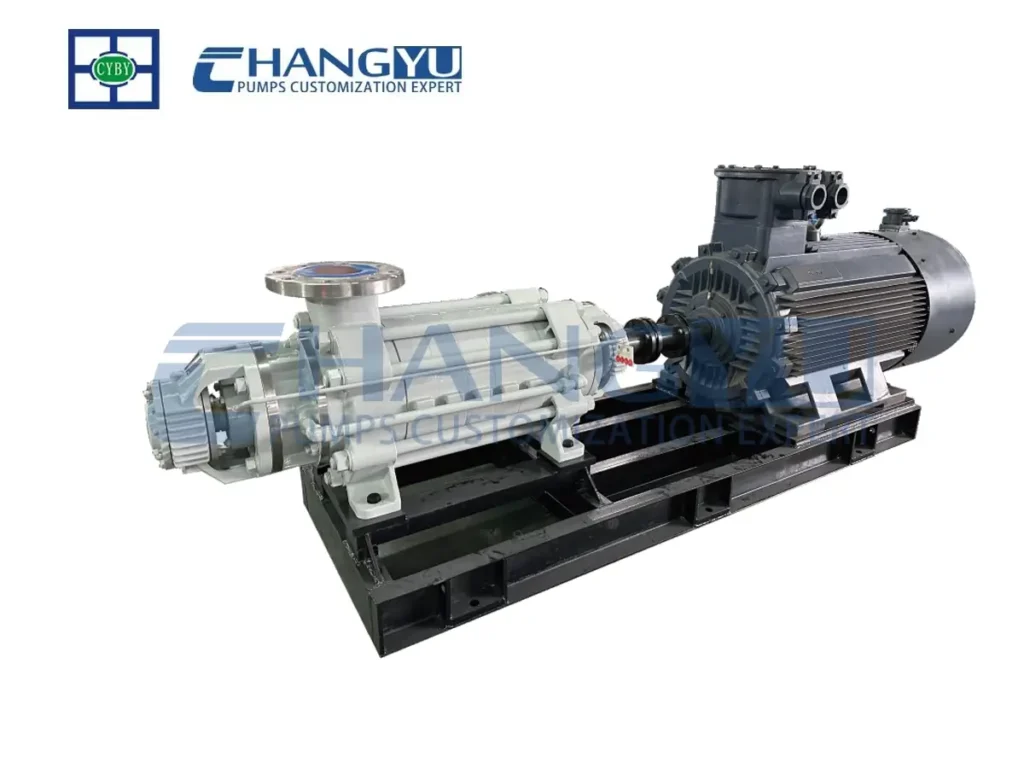
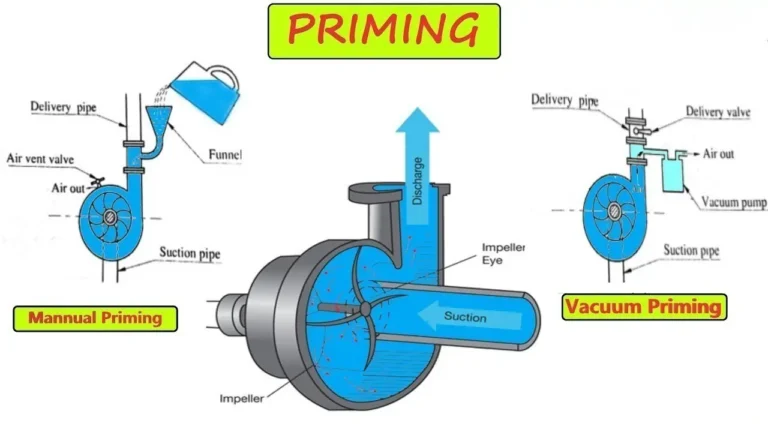
A centrifugal pump is a pumping device that uses a motor to drive the impeller to rotate, generating centrifugal force, giving the liquid kinetic energy, and then converting the kinetic energy into pressure energy through the pump casing, finally delivering the liquid to the target location.
Common types include:
- Submersible Pump: Can work submerged in liquid, suitable for mine drainage, wastewater treatment, and other deep water applications.
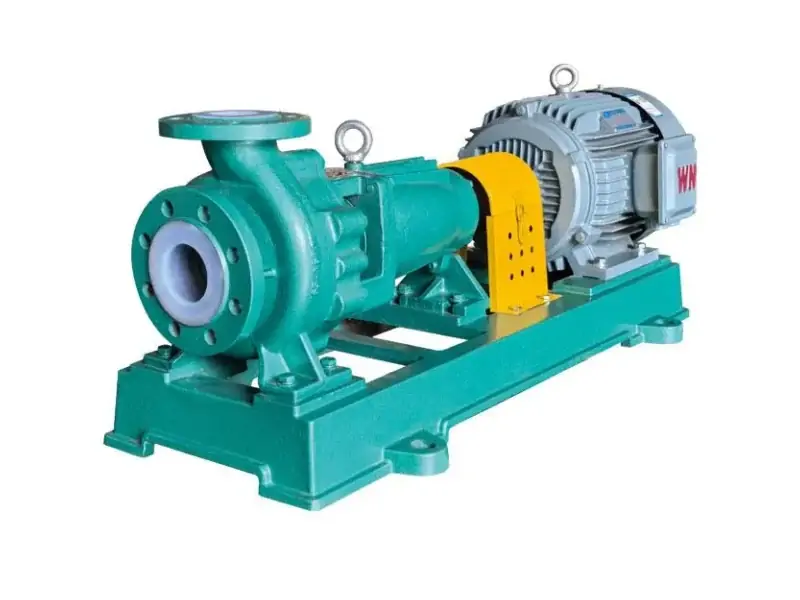
- End Suction Pump: Compact structure, suitable for conventional flow and head requirements.
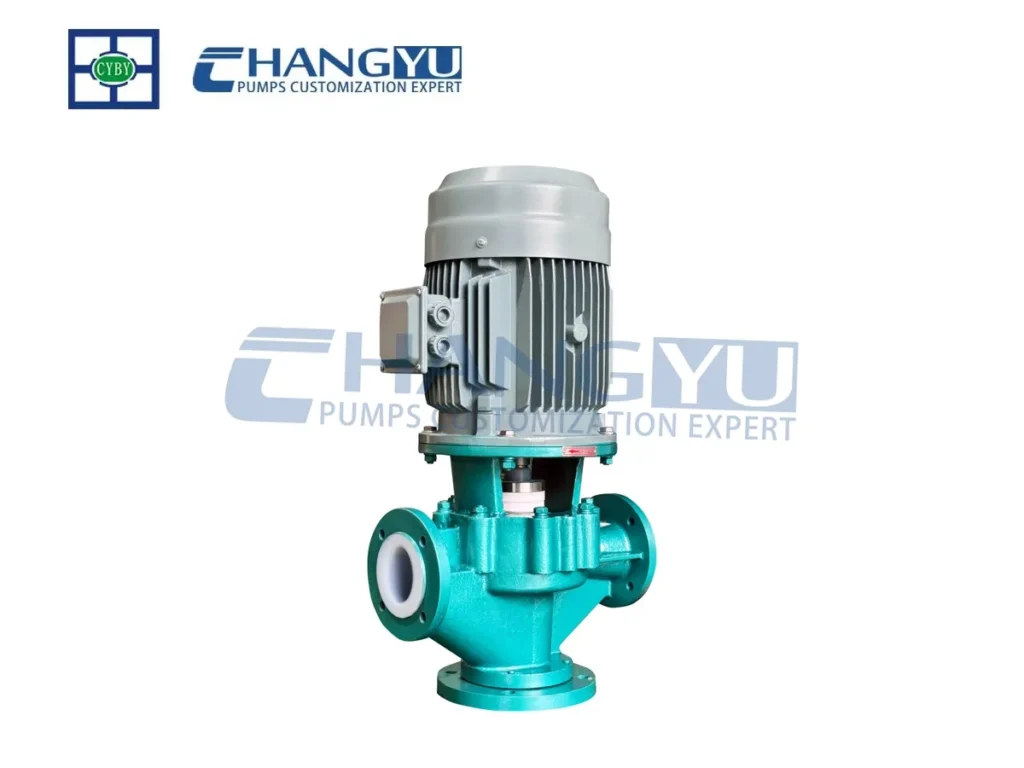
- Pipeline Pump (Vertical Pump): Inline structure, can be directly installed in pipelines, used for heating, air conditioning, and other circulation systems.
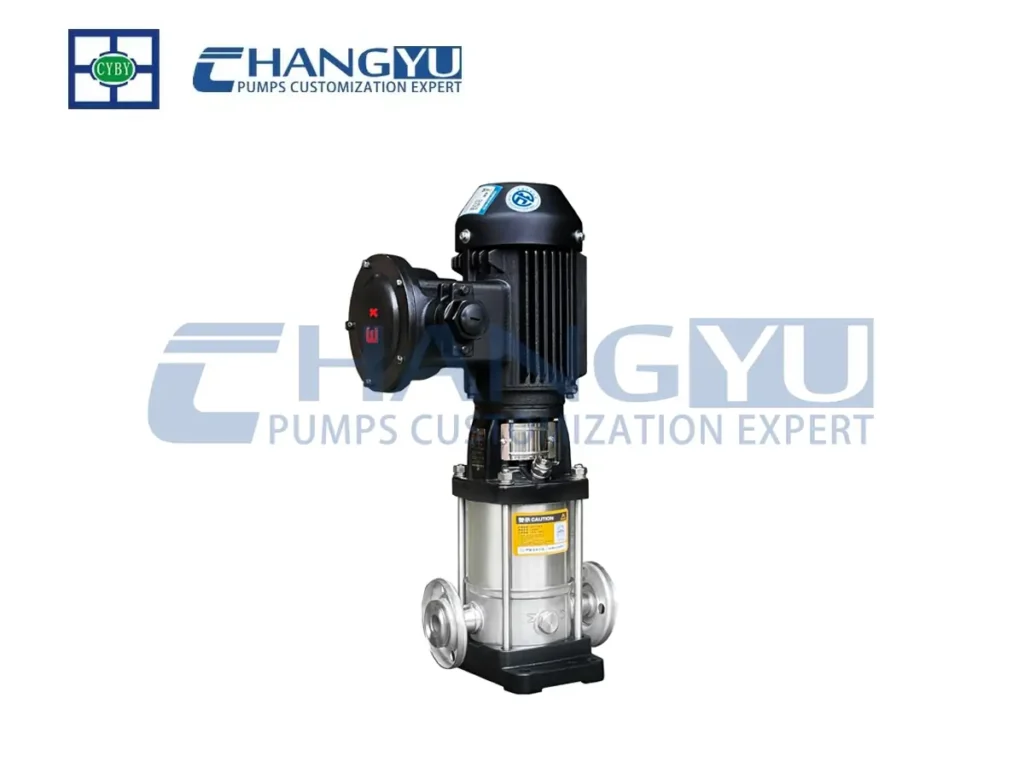
- Multistage Pump: Multiple impellers in series, can significantly increase outlet pressure, suitable for high-pressure water supply, fire fighting, etc.
- Bomba auto-ferrante: Can start without pre-filling, solving the suction limitation of ordinary centrifugal pumps.
What is a Positive Displacement Pump?
A Positive Displacement Pump delivers fluid by the periodic change of the working chamber volume, such as piston reciprocation or gear meshing, similar to “squeezing toothpaste,” discharging a fixed volume of fluid each time.
Common types include:
- Gear Pump: Uses two intermeshing gears to form volume changes to deliver liquid, suitable for hydraulic systems, lubrication oil, fuel delivery, and can also handle high-temperature (above 400℃) or molten media.
- Screw Pump: Uses the meshing of main and secondary screws to form helical sealed chambers, delivering continuously by rotation, suitable for high-viscosity or solid-containing media, such as crude oil and slurry.
- Plunger/Piston Pump: Uses plunger or piston reciprocation in the pump cylinder to change volume and deliver fluid, suitable for high-pressure cleaning, oilfield water injection, and hydraulic systems.
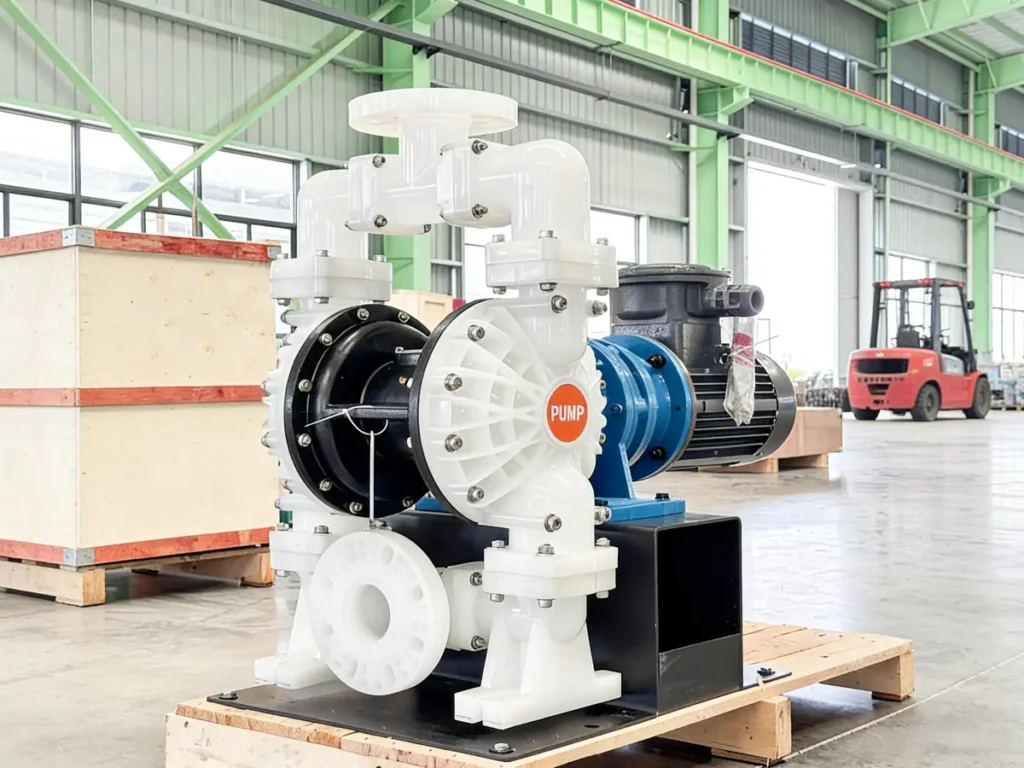
- Bomba de diafragma: Uses diaphragm reciprocation to change chamber volume, completely isolating the medium from the driving mechanism, suitable for corrosive liquids and high-safety scenarios in food and pharmaceutical industries.
Centrifugal Pump VS Positive Displacement Pump
Below, we show the differences between the Bomba centrífuga and the Positive Displacement Pump from different perspectives:
| Feature | Bomba centrífuga | Positive Displacement Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Princípio de funcionamento | Generates centrifugal force through high-speed impeller rotation, converting mechanical energy into liquid kinetic energy and pressure energy | Delivers liquid by changing pump chamber volume (gear, screw, plunger, diaphragm, etc.) |
| Flow Characteristics | Flow is closely related to outlet pressure; when pressure increases, flow decreases significantly | Flow is almost independent of outlet pressure, only related to speed and displacement; flow is basically stable under high pressure (may slightly decrease due to leakage) |
| Pressure Characteristics | Outlet pressure depends on impeller speed, structure, and flow; there is a “rated pressure” range, exceeding which flow drops sharply, and pressure cannot continue to rise | Theoretically, outlet pressure can increase indefinitely with system resistance (e.g., valve throttling or pipeline blockage), but actual maximum pressure is limited by pump strength, sealing, and power |
| Suitable Media | Clean water, low-viscosity liquids; materials can be selected for media with solid content below 35% or corrosive media | High-viscosity liquids, media containing solid particles or corrosive liquids |
| Structural Features | Impeller rotates; pump passage transmits pressure; fewer moving parts | Positive displacement pumps have meshing or reciprocating parts; structure is relatively complex |
| Startup Requirement | Requires priming | Most self-priming or no priming required (e.g., screw pump, diaphragm pump) |
| Efficiency Characteristics | High efficiency at high flow and low viscosity; efficiency decreases as viscosity increases | High efficiency for high-viscosity liquids; slightly lower efficiency for low-viscosity liquids |
| Typical Applications | Industrial circulating water, air conditioning, agricultural irrigation, fire fighting, high-pressure water supply | Hydraulic oil, crude oil, chemical slurry, high-pressure cleaning, corrosive liquid delivery |
| Maintenance | Fewer moving parts, simple maintenance | Seals, sliding/meshing parts require regular maintenance or replacement |
| Typical Pump Types | Single-stage centrifugal pump, multistage pump, end suction pump, self-priming pump, submersible pump | Gear pump, screw pump, plunger pump, diaphragm pump |
Through the above table, Changyu Pump explains the differences between the two pump types. Therefore, the answer to “Are centrifugal pumps positive displacement?” is clearly no. They are two different types of pumps.
Aplicação
Bomba centrífuga
Centrifugal pumps are called the “heart of modern industry.” Application scenarios include:
- Industrial: Petrochemical, coal chemical, power (circulating water supply), etc.
- Municipal and Agriculture: Urban water supply, wastewater treatment, agricultural irrigation.
- Special Applications: Sterile delivery in pharmaceutical industry, beverage transfer in food industry, etc.
Positive Displacement Pump
- High-Viscosity Fluids: Food industry syrup or chocolate delivery, petroleum industry asphalt or lubrication oil.
- Gas-containing / Gas-Liquid Mixed Fluids: Chemical industry solvent vapor, biogas, or handling easily vaporizing liquids (e.g., propane).
- Metering & Distribution: Pharmaceutical precise dosing, paint industry quantitative feeding.
- High-Pressure Scenarios: Hydraulic systems (e.g., excavators, injection molding machines), high-pressure cleaning equipment.
Changyu Pump Selection Suggestions
- Prefer Centrifugal Pump: When large flow, low viscosity, clean liquids, and stable system pressure are needed (e.g., cooling circulation, irrigation).
- Prefer Positive Displacement Pump: When high pressure, high viscosity, gas/solid-containing fluid, or precise metering is needed (e.g., hydraulic systems, paint delivery).
Conclusão
The answer to “is a centrifugal pump a positive displacement pump?” is NO.
They are two different working principles with different application scenarios. If you have any questions about pump selection or fluid handling, you can contact us now. Our professional team will guide your selection and provide the latest pumping solutions.
Correio eletrónico: jade@changyupump.com
Phone: +86-13651913727